East Africa's capital cities are the political and economic centers of their respective countries, playing a vital role in the region's development and progress.
These cities are home to government institutions, major businesses, and cultural landmarks, making them hubs of activity and influence. They offer a unique blend of modern infrastructure and rich historical heritage, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of East Africa.
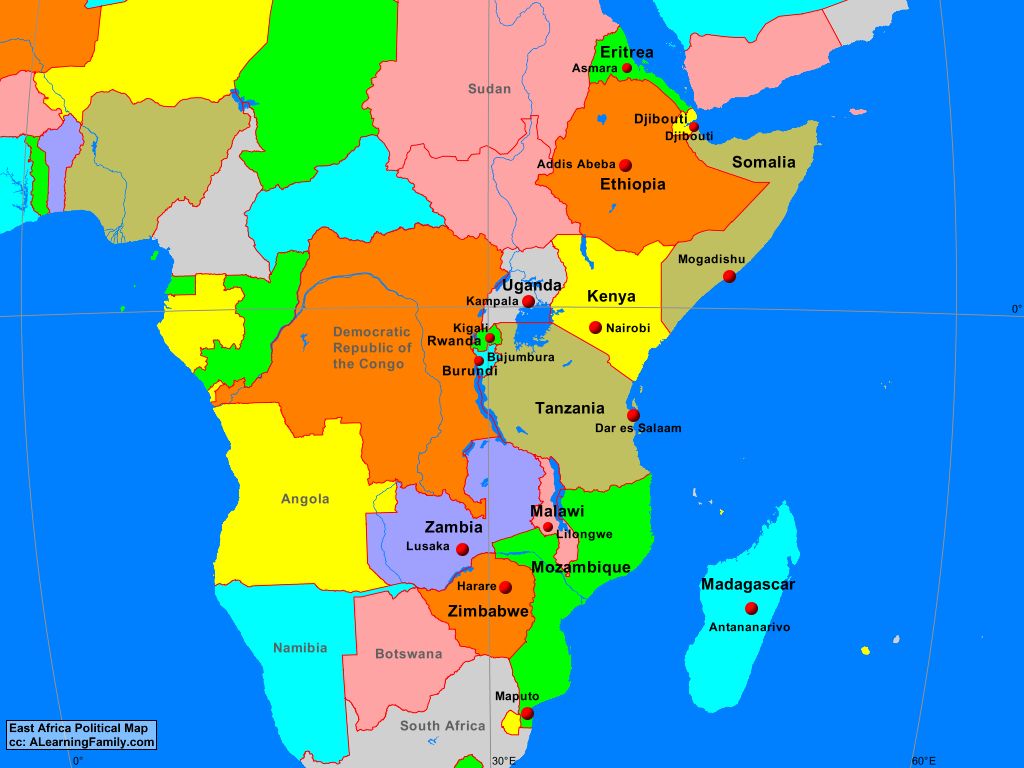
Some of the most prominent East African capital cities include Nairobi (Kenya), Kampala (Uganda), Dar es Salaam (Tanzania), Kigali (Rwanda), and Addis Ababa (Ethiopia). Each city has its own distinct character and charm, contributing to the region's cultural tapestry and economic growth.
East Africa Capital Cities
East Africa's capital cities are vibrant and dynamic centers of political, economic, and cultural activity. They offer a unique blend of modern infrastructure and rich historical heritage, reflecting the diverse and dynamic nature of the region.
- Political Centers: East Africa's capital cities are the seats of government and house key political institutions, playing a vital role in shaping the region's political landscape.
- Economic Hubs: These cities are major centers of commerce and industry, attracting businesses and investments from across the region and beyond.
- Cultural Melting Pots: East Africa's capital cities are home to a diverse population, reflecting the region's rich cultural heritage and fostering a vibrant arts and cultural scene.
- Infrastructure Gateways: These cities are often major transportation hubs, with international airports and seaports connecting them to the rest of the world.
- Historical Significance: Many East African capital cities have a long and fascinating history, with landmarks and monuments that tell the story of the region's past.
- Population Centers: East Africa's capital cities are home to a significant proportion of the region's population, making them important centers of urban development and planning.
- Regional Cooperation: These cities play a key role in fostering regional cooperation and integration, hosting international organizations and summits.
- Development Drivers: East Africa's capital cities are engines of economic growth and development, driving innovation and attracting investment in key sectors.
- Future Potential: These cities have immense potential for continued growth and development, playing a vital role in shaping the future of East Africa.
In conclusion, East Africa's capital cities are multifaceted and dynamic centers that play a crucial role in the region's political, economic, cultural, and social development. They are gateways to the region's rich history, vibrant present, and promising future.
Political Centers
East Africa's capital cities are the political nerve centers of their respective countries, housing the key institutions and government bodies that govern and administer the region. These cities are where political decisions are made, laws are enacted, and policies are implemented, shaping the political landscape and direction of East Africa.
- National Parliaments and Legislatures: Capital cities are home to national parliaments and legislatures, the elected bodies that represent the people and enact laws. These institutions play a crucial role in shaping the political agenda and ensuring accountability and transparency in governance.
- Presidential Palaces and Executive Offices: The official residences and offices of presidents and heads of state are often located in capital cities, symbolizing the seat of executive power and authority. From these centers, leaders oversee the day-to-day administration of the country and make key policy decisions.
- Ministries and Government Departments: Ministries and government departments responsible for various sectors, such as finance, foreign affairs, and justice, are typically headquartered in capital cities. These institutions coordinate and implement government policies, ensuring the smooth functioning of the state.
- Courts and Legal Institutions: High courts, supreme courts, and other legal institutions are often located in capital cities, serving as the guardians of justice and the rule of law. These institutions adjudicate disputes, interpret laws, and uphold constitutional rights.
In conclusion, the political centrality of East Africa's capital cities is a key aspect of their role and influence in the region. As the seats of government and key political institutions, these cities are the epicenters of political power and decision-making, shaping the political landscape and direction of East Africa.
Economic Hubs
East Africa's capital cities are not only political centers but also major economic hubs, attracting businesses and investments from across the region and beyond. This economic vitality is closely tied to their status as capital cities, which offers several advantages:
- Central Location and Infrastructure: Capital cities are often centrally located within their respective countries, with well-developed infrastructure, including transportation networks, communication systems, and utilities. This makes them ideal locations for businesses to establish their operations and reach a wider market.
- Access to Government and Institutions: Being the seats of government, capital cities provide businesses with direct access to government officials, regulatory bodies, and financial institutions. This proximity facilitates business registration, licensing, and other administrative processes.
- Skilled Workforce and Talent Pool: Capital cities attract skilled workers and professionals from across the country, creating a large talent pool for businesses to tap into. This availability of human capital is crucial for economic growth and innovation.
- Regional and International Connections: As capital cities, these urban centers are often the main gateways to their respective countries and the wider East African region. They have international airports and seaports, connecting businesses to global markets and supply chains.
The economic importance of East Africa's capital cities is evident in the presence of major corporations, financial institutions, and international organizations. These cities are home to stock exchanges, banks, and insurance companies, playing a vital role in the region's financial sector. They also attract foreign direct investment, contributing to economic growth and development.
In conclusion, the economic vitality of East Africa's capital cities is closely intertwined with their status as political centers. These cities offer a unique combination of central location, access to government and institutions, skilled workforce, and regional and international connections, making them attractive destinations for businesses and investments.
Cultural Melting Pots
East Africa's capital cities are melting pots of culture, where diverse ethnic groups, traditions, and languages converge. This cultural diversity is a defining characteristic of these urban centers and contributes to their unique charm and vibrancy.
- Diversity and Inclusion: Capital cities attract people from all walks of life, creating a diverse and inclusive environment. This mix of cultures fosters understanding, tolerance, and appreciation of different perspectives.
- Cultural Heritage and Identity: Capital cities often serve as custodians of a nation's cultural heritage. They house museums, historical landmarks, and cultural institutions that preserve and celebrate the region's rich traditions and identity.
- Arts and Cultural Scene: The cultural melting pot of capital cities nourishes a thriving arts and cultural scene. These cities are hubs for artists, musicians, dancers, and performers, offering a wide range of cultural experiences, from traditional folk art to contemporary urban expressions.
- Cultural Exchange and Innovation: The convergence of diverse cultures in capital cities creates opportunities for cultural exchange and innovation. Artists and creatives draw inspiration from multiple sources, leading to the emergence of new and exciting cultural forms.
The cultural melting pot aspect of East Africa's capital cities is not only a source of pride but also a driving force for social cohesion and economic development. By embracing diversity and fostering a vibrant cultural scene, these cities contribute to the overall well-being and progress of the region.
Infrastructure Gateways
East Africa's capital cities serve as crucial infrastructure gateways, connecting the region to the rest of the world through international airports and seaports. This connectivity plays a vital role in the economic and social development of these cities and the broader East African region.
The presence of international airports in capital cities facilitates trade, tourism, and investment. Direct flights to major global destinations enable businesses to access international markets, attract foreign investment, and promote economic growth. For example, the Jomo Kenyatta International Airport in Nairobi, Kenya, serves as a major hub for East and Central Africa, connecting the region to Europe, Asia, and the Middle East.
Seaports are equally important for East Africa's capital cities, providing access to maritime trade routes and facilitating the import and export of goods. The Port of Dar es Salaam in Tanzania is a key gateway for the region, handling a significant portion of East Africa's trade with Asia, Europe, and the Americas. These seaports also serve as hubs for regional shipping and logistics, supporting the movement of goods within East Africa.
The role of East Africa's capital cities as infrastructure gateways extends beyond economic benefits. International airports and seaports also facilitate cultural exchange, tourism, and people-to-people connections. They enable people from East Africa to travel abroad for education, business, and leisure, while also making the region more accessible to international visitors.
In conclusion, the status of East Africa's capital cities as infrastructure gateways is a critical factor in their development and prosperity. By connecting the region to the rest of the world, these cities play a vital role in trade, investment, tourism, and cultural exchange, contributing to the overall economic and social progress of East Africa.
Historical Significance
The historical significance of East Africa's capital cities is deeply intertwined with the development and identity of these urban centers. Many of these cities have a rich and storied past, with landmarks and monuments that serve as tangible reminders of the region's cultural heritage and historical events.
One prominent example is Addis Ababa, the capital of Ethiopia. Founded in the late 19th century by Emperor Menelik II, the city is home to numerous historical sites, including the National Museum of Ethiopia, which houses a vast collection of artifacts and exhibits showcasing the country's ancient and medieval history. Another notable landmark is the Holy Trinity Cathedral, a stunning example of Ethiopian Orthodox architecture that played a central role in the country's religious and political life.
Similarly, Dar es Salaam, the former capital of Tanzania, boasts a rich history dating back to the 19th century. The city's historic architecture reflects the diverse cultural influences that have shaped its development, including Arab, Indian, and European influences. One of the most iconic landmarks is the Askari Monument, a war memorial commemorating the fallen soldiers of the King's African Rifles during World War I.
The historical significance of East Africa's capital cities extends beyond individual landmarks and monuments. The very layout and structure of these cities often tell a story of their past. For example, the grid-like street plan of Nairobi, Kenya, reflects the city's colonial origins as a British administrative center. In contrast, the winding streets and traditional architecture of Zanzibar Stone Town, Tanzania, evoke the city's rich Swahili heritage and history as a major trading hub.
Understanding the historical significance of East Africa's capital cities is not only important for preserving and appreciating the region's cultural heritage but also for shaping its future development. By recognizing the historical roots of these cities, policymakers and urban planners can make informed decisions that respect and enhance their unique character and identity.
Population Centers
The population concentration in East Africa's capital cities is a defining characteristic that shapes their role and significance in the region. These cities are not only political, economic, and cultural hubs but also major centers of urban development and planning.
The high population density in capital cities is primarily driven by the concentration of economic opportunities and services. As the seats of government and major businesses, capital cities offer employment, education, healthcare, and other amenities that attract people from rural areas and smaller towns. This influx of population leads to urban growth, which in turn requires comprehensive planning and development strategies.
Urban planners in East Africa's capital cities face the challenge of managing rapid urbanization while ensuring sustainable development. They must plan for adequate housing, transportation systems, infrastructure, and public services to accommodate the growing population. This includes addressing issues such as informal settlements, traffic congestion, and environmental pollution.
Understanding the importance of population centers in East Africa's capital cities is crucial for effective urban planning and governance. By recognizing the unique challenges and opportunities associated with high population density, policymakers can develop policies and strategies that promote economic growth, social equity, and environmental sustainability in these vital urban centers.
Regional Cooperation
East Africa's capital cities serve as hubs for regional cooperation and integration, hosting international organizations and summits that bring together leaders and representatives from across the region. This role is vital in promoting economic development, political stability, and social progress in East Africa.
The presence of regional organizations and institutions in capital cities facilitates dialogue, collaboration, and joint initiatives among East African countries. For example, Nairobi, the capital of Kenya, is the headquarters of the East African Community (EAC), a regional bloc that promotes economic integration, infrastructure development, and political cooperation among its member states.
Furthermore, East Africa's capital cities often host international summits and conferences that bring together regional and global leaders to address common challenges and opportunities. These events provide platforms for discussing issues such as trade, security, climate change, and sustainable development, fostering consensus and collective action.
The role of East Africa's capital cities in fostering regional cooperation has significant practical implications. It strengthens regional bonds, promotes economic growth, and enhances the region's voice in global affairs. By working together, East African countries can leverage their collective resources and expertise to address shared challenges and achieve common goals.
In conclusion, the connection between East Africa's capital cities and regional cooperation is crucial for the development and prosperity of the region. By hosting international organizations and summits, these cities serve as platforms for dialogue, collaboration, and collective action, contributing to economic integration, political stability, and social progress in East Africa.
Development Drivers
East Africa's capital cities play a pivotal role as development drivers, propelling economic growth, fostering innovation, and attracting investment in key sectors. This dynamic relationship between capital cities and development is multifaceted, encompassing several key facets:
- Economic Hubs: Capital cities are centers of commerce and industry, attracting businesses, investors, and entrepreneurs. They provide a concentrated market for goods and services, stimulating economic activity and job creation.
- Infrastructure and Connectivity: Capital cities typically boast superior infrastructure, including transportation networks, telecommunications systems, and utilities. This connectivity enhances business operations, facilitates trade, and attracts foreign direct investment.
- Innovation and Knowledge Centers: Capital cities often host universities, research institutions, and technology hubs. This concentration of knowledge and expertise fosters innovation, drives technological advancements, and creates a skilled workforce.
- Policy and Regulatory Frameworks: Capital cities are home to government institutions and regulatory bodies that establish economic policies and regulations. These frameworks shape the investment climate, influence business decisions, and promote economic growth.
The convergence of these factors in East Africa's capital cities creates a virtuous cycle of economic development. They attract businesses and investments, which in turn generate jobs, boost innovation, and improve infrastructure. This positive feedback loop contributes to the overall prosperity and competitiveness of the region.
Future Potential
The capital cities of East Africa stand as beacons of progress and opportunity, possessing immense potential to drive further growth and development in the region. This potential stems from several key factors that position these cities as engines of economic prosperity and social advancement:
- Innovation Hubs: Capital cities are often centers of innovation, attracting skilled professionals, researchers, and entrepreneurs. This concentration of talent fosters the development of new technologies, products, and services, contributing to economic diversification and job creation.
- Investment Gateways: As political and economic centers, capital cities attract domestic and foreign investment. This influx of capital fuels infrastructure development, business expansion, and the creation of new industries, leading to sustained economic growth.
- Improved Infrastructure: Capital cities prioritize infrastructure development to support economic activity and improve the quality of life for residents. Investments in transportation, energy, and communication networks enhance connectivity, reduce business costs, and attract investment.
- Human Capital Development: Capital cities are home to leading educational institutions and training centers, producing a highly skilled workforce. This skilled labor force is essential for driving innovation, attracting investment, and ensuring the long-term competitiveness of the region.
By harnessing these factors, East Africa's capital cities can unlock their full potential and play a pivotal role in shaping the future of the region. They can become engines of economic growth, innovation, and social progress, transforming East Africa into a prosperous and thriving hub.
Frequently Asked Questions about East Africa Capital Cities
This section addresses some common questions and misconceptions about East Africa's capital cities, providing concise and informative answers.
Question 1: What are the major capital cities in East Africa?
Answer: The major capital cities in East Africa include Nairobi (Kenya), Kampala (Uganda), Dar es Salaam (Tanzania), Kigali (Rwanda), and Addis Ababa (Ethiopia).
Question 2: What is the significance of capital cities in East Africa?
Answer: East Africa's capital cities are political, economic, cultural, and infrastructural hubs, playing vital roles in the region's development and progress.
Question 3: How do capital cities contribute to regional cooperation in East Africa?
Answer: Capital cities host international organizations and summits, facilitating dialogue, collaboration, and collective action among East African countries.
Question 4: What are the key economic drivers in East Africa's capital cities?
Answer: Capital cities attract businesses, investments, and skilled labor, driving innovation, economic growth, and job creation.
Question 5: How are capital cities addressing the challenges of rapid urbanization?
Answer: Urban planners focus on sustainable development strategies, providing adequate housing, transportation, infrastructure, and public services to accommodate growing populations.
Question 6: What is the future outlook for East Africa's capital cities?
Answer: Capital cities possess immense potential for continued growth and development, driven by innovation, investment, infrastructure improvements, and human capital development.
Summary: East Africa's capital cities are dynamic and multifaceted centers that play crucial roles in the region's political, economic, cultural, and social development. They are hubs of innovation, investment, and regional cooperation, driving progress and shaping the future of East Africa.
Transition to the next article section: To delve deeper into the specific characteristics and contributions of each capital city, explore the following sections:
Tips for Understanding East Africa Capital Cities
To gain a deeper understanding of East Africa's capital cities, consider these informative tips:
Tip 1: Explore Their Historical Significance
Delve into the rich history of these cities to appreciate their architectural landmarks, cultural heritage, and the role they played in shaping the region's past.
Tip 2: Immerse Yourself in the Local Culture
Visit local markets, attend traditional festivals, and interact with the diverse communities to experience the vibrant and unique cultures that define each city.
Tip 3: Leverage Their Economic Importance
Recognize the significant economic contributions of these cities as hubs of commerce, industry, and innovation, driving regional growth and development.
Tip 4: Appreciate Their Infrastructure Advantages
Modern infrastructure, including international airports and seaports, connects these cities to the world, facilitating trade, tourism, and cultural exchange.
Tip 5: Engage with the Local Population
Interact with the friendly and welcoming locals to gain insights into their daily lives, perspectives, and the challenges and opportunities they face.
Summary: By following these tips, you will develop a more comprehensive understanding and appreciation of East Africa's capital cities, their unique characteristics, and their vital contributions to the region.
Transition to the conclusion: These capital cities stand as testaments to the rich history, cultural diversity, and economic dynamism of East Africa. As you explore and engage with them, you will gain a deeper appreciation for their significance and the role they play in shaping the future of the region.
Conclusion
Our exploration of East Africa's capital cities has unveiled their multifaceted nature and profound significance. These urban centers are not merely political and administrative hubs, but vibrant melting pots of culture, innovation, and economic growth.
Their historical roots have shaped their unique identities, from the ancient architecture of Addis Ababa to the cosmopolitan streets of Nairobi. The convergence of diverse communities within these cities has fostered a rich tapestry of traditions, languages, and artistic expressions.
As economic powerhouses, East Africa's capital cities attract businesses, investments, and skilled professionals. Their modern infrastructure and connectivity to the world stage facilitate trade, tourism, and the exchange of ideas.
Moreover, these cities play a vital role in regional cooperation, hosting international organizations and summits that address common challenges and promote collaboration.
As we look to the future, East Africa's capital cities stand poised for continued growth and development. They have the potential to become even more dynamic hubs of innovation, sustainability, and cultural exchange.
By embracing their unique strengths and addressing the challenges they face, these cities can harness their potential to drive progress and prosperity for the entire East African region.
Detail Author:
- Name : Prof. John Grimes
- Username : catharine.brown
- Email : hickle.margarete@yahoo.com
- Birthdate : 1986-08-09
- Address : 92934 Jenkins Walks New Robbie, MI 35194
- Phone : 1-971-493-5278
- Company : Roob Ltd
- Job : Heaters
- Bio : Accusantium voluptatem corrupti neque ea nulla id nihil omnis. Totam culpa aut qui nisi assumenda et. Esse molestiae omnis doloribus amet. Cumque error corporis et atque earum non natus.
Socials
tiktok:
- url : https://tiktok.com/@mustafa.turner
- username : mustafa.turner
- bio : Quis sapiente aperiam sunt nam suscipit nemo.
- followers : 4963
- following : 105
twitter:
- url : https://twitter.com/turner1984
- username : turner1984
- bio : Quis et aspernatur laudantium placeat. Dolores placeat sit consequatur ut non.
- followers : 265
- following : 2918
facebook:
- url : https://facebook.com/mustafaturner
- username : mustafaturner
- bio : Explicabo rerum sed non eius deleniti alias quia ut.
- followers : 6539
- following : 1104